Table Of Content
In a between-subjects design (also known as an independent measures design or classic ANOVA design), individuals receive only one of the possible levels of an experimental treatment. For valid conclusions, you also need to select a representative sample and control any extraneous variables that might influence your results. If if random assignment of participants to control and treatment groups is impossible, unethical, or highly difficult, consider an observational study instead.
Methodology
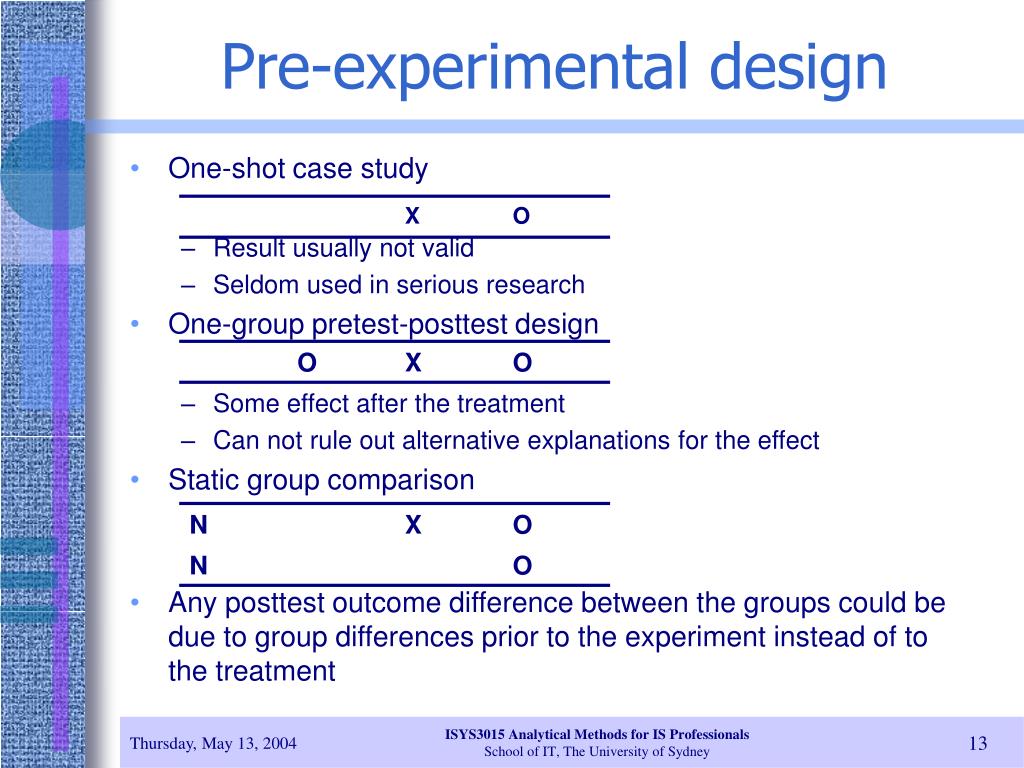
Determine which type of stimulus meets your experiment’s needs and how widely or finely to vary your stimuli. This research method introduces a single test group to a single stimulus to study the results at the end of the application. During research, you observe one or more groups after applying a treatment to test whether the treatment causes any change. However, these conditions are unethical or impossible to achieve in some situations.
Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies
Therefore, we can conclude that sunlight will aid growth in all similar plants. Others, like Sequential Design, are flexible and adaptable, making quick changes based on what they learn. And let's not forget the adventurous Field Experiments, which take us out of the lab and into the real world to discover things we might not see otherwise.

Insufficient or Incorrect Statistical Analysis
A research study could conduct pre-experimental research design when a group or many groups are under observation after implementing factors of cause and effect of the research. The pre-experimental design will help researchers understand whether further investigation is necessary for the groups under observation. To publish significant results, choosing a quality research design forms the foundation to build the research study. Moreover, effective research design helps establish quality decision-making procedures, structures the research to lead to easier data analysis, and addresses the main research question. Therefore, it is essential to cater undivided attention and time to create an experimental research design before beginning the practical experiment. This is because it takes place in a real-life setting, where extraneous variables cannot be eliminated.
Experimental studies of conflict: Challenges, solutions, and advice to junior scholars - Shorenstein Center
Experimental studies of conflict: Challenges, solutions, and advice to junior scholars.
Posted: Wed, 28 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Cluster Randomized Design
The purpose of experimental design is to control and manipulate one or more independent variables to determine their effect on a dependent variable. Experimental design allows researchers to systematically investigate causal relationships between variables, and to establish cause-and-effect relationships between the independent and dependent variables. Through experimental design, researchers can test hypotheses and make inferences about the population from which the sample was drawn. When done using true experimental design, causality can be infered, which allows researchers to provide proof that an independent variable affects a dependent variable.
Basically, a researcher can conduct experimental research any time they want to test a theory with variable and dependent controls. This design allows researchers to conduct a similar experiment by assigning subjects to groups based on non-random criteria. Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Within-Subjects Experiments
Finding two groups of participants that match all the key characteristics that might influence your results can be difficult. For example, participants may perform better in the second condition because they know the task already (practise effect) or may not perform as well due to fatigue (fatigue effect). Results must be counted or measured in some way so that discrete information can be obtained. In the aspirin example, the number of people who develop heart disease is counted as well as the age at which signs of heart disease are apparent. The variance of the estimate X1 of θ1 is σ2 if we use the first experiment.
Randomization vs Random Selection
Regression analysis is used to model the relationship between two or more variables in order to determine the strength and direction of the relationship. There are several types of regression analysis, including linear regression, logistic regression, and multiple regression. Behavioral measures involve measuring participants’ behavior directly, such as through reaction time tasks or performance tests.
How do I tell if my article is a Randomized Control Trial?
For instance, if we want to determine whether expressive writing affects people’s health then we could start by measuring various health-related variables in our prospective research participants. We could then use that information to rank-order participants according to how healthy or unhealthy they are. The next two healthiest participants would then be randomly assigned to complete different conditions, and so on until the two least healthy participants. This method would ensure that participants in the traumatic experiences writing condition are matched to participants in the neutral writing condition with respect to health at the beginning of the study. If at the end of the experiment, a difference in health was detected across the two conditions, then we would know that it is due to the writing manipulation and not to pre-existing differences in health.
Double-Blind Studies in Research - Verywell Mind
Double-Blind Studies in Research.
Posted: Wed, 12 Apr 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
This is when participants are paired in terms of specific characteristics such as age or ethnicity. When it comes to experimental designs, one size doesn't fit all, and choosing the right one for your research is crucial. A design that works great in one context won't necessarily be the appropriate choice for a different study. In this article, we'll go through experimental designs in psychology, consider the strengths and weaknesses of each one and consider what contexts they could be applied in.
For example, if ten different studies show that a certain medicine helps lower blood pressure, a meta-analysis would pull all that information together to give a more accurate answer. The correlational design has roots in the early days of psychology and sociology. Pioneers like Sir Francis Galton used it to study how qualities like intelligence or height could be related within families. Now, let's flip the script and talk about Cross-Sectional Design, the polar opposite of the Longitudinal Design. If Longitudinal is the grand storyteller, think of Cross-Sectional as the snapshot photographer. It captures a single moment in time, like a selfie that you take to remember a fun day.
One of the most famous correlational studies you might have heard of is the link between smoking and lung cancer. Back in the mid-20th century, researchers started noticing that people who smoked a lot also seemed to get lung cancer more often. They couldn't say smoking caused cancer—that would require a true experiment—but the strong correlation was a red flag that led to more research and eventually, health warnings. Despite these challenges, longitudinal studies have been key in fields like psychology, sociology, and medicine. They provide the kind of deep, long-term insights that other designs just can't match. This design's main selling point is its ability to explore interactions between variables.

Mostly related to a laboratory test procedure, experimental research designs involve collecting quantitative data and performing statistical analysis on them during research. Pre-Experimental Designs are the basic, no-frills versions of experiments. Researchers still mess around with an independent variable and measure a dependent variable, but they skip over the whole randomization thing and often don't even have a control group.
No matter the kind of absurd behavior that is exhibited by the subject during this period, its condition will not be changed. The choice of setting used in research depends on the nature of the experiment being carried out. In a static-group comparison study, 2 or more groups are placed under observation, where only one of the groups is subjected to some treatment while the other groups are held static. All the groups are post-tested, and the observed differences between the groups are assumed to be a result of the treatment. This research design combines both posttest and pretest study by carrying out a test on a single group before the treatment is administered and after the treatment is administered.


No comments:
Post a Comment